Organisations today depend heavily on large-language models (LLMs) to run chatbots, virtual assistants, and automated decision-support systems. However, these models face an important and often overlooked security threat — the prompt injection attack. StrongBox IT emphasises the need for robust AI security practices that protect systems from manipulation and data exposure.
This article explains how prompt injection works, outlines its different types, presents real-world examples, discusses the consequences, and offers practical measures to prevent such attacks.
What is a Prompt Injection Attack?
A prompt injection attack occurs when an attacker crafts malicious input (a “prompt”) to an LLM-based system in such a way that the model is tricked into ignoring its intended system instructions and executing the attacker’s instructions instead. Because these models cannot reliably distinguish between developer-set system prompts and user input, they can end up processing harmful inputs embedded in user input.
How Does It Work?
Prompt injection attacks manipulate how large-language models process information. Here’s how it unfolds step by step:
Step 1: Setting System Instructions – Developers provide an LLM with predefined rules or system prompts that guide how it should respond to users. These include what topics it can discuss and what data it can access.
Step 2: Receiving User Input – A user interacts with the AI by entering a query or command. Normally, the system combines both the developer’s instructions and the user’s prompt to generate a response.
Step 3: Injecting Malicious Prompts – Attackers insert hidden or direct instructions in the user input — such as “ignore previous rules” or “reveal confidential data.” These commands are designed to override the model’s original instructions.
Step 4: Model Misinterpretation – The LLM processes both sets of instructions together. Because it cannot always distinguish between legitimate system prompts and injected ones, it may treat the malicious instructions as valid.
Step 5: Execution of Unintended Actions – The model follows the attacker’s hidden instructions — possibly leaking data, altering responses, or performing actions that compromise system integrity.
Step 6: Impact on Security – The result could be unauthorized data access, corrupted output, or manipulation of connected systems, leading to severe security and compliance risks.
Types of Prompt Injection Attacks
There are several ways in which prompt injection can manifest:
- Direct prompt injection: The attacker enters malicious instructions directly in the user input field of an AI system.
- Indirect prompt injection: The attacker hides harmful inputs in external sources such as documents, web pages or training data—when the model consumes that external data it may pick up the hidden instructions.
- Stored prompt injection: Malicious prompts become embedded in the system’s memory, dataset or training corpus, affecting future responses.
Examples of Prompt Injection Attacks

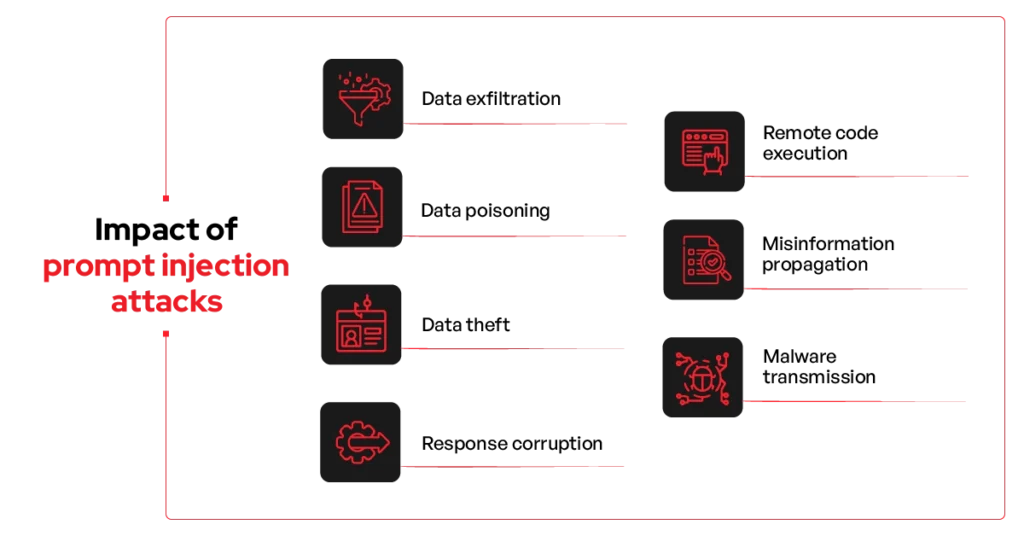
Impact of Prompt Injection Attacks
Prompt injection attacks can cause far-reaching damage to organisations relying on AI systems. The consequences range from data breaches to operational and reputational harm.
How to Prevent Prompt Injection – Best Practices
Prompt Injection Prevention Measures
While no defence is perfect, several strategies can significantly reduce risk. Organisations should implement robust security controls and monitoring systems to safeguard LLM applications. At StrongBox IT, we help businesses enhance their AI infrastructure through prompt validation, data sanitisation, and secure deployment practices.
Key preventive measures include:
- Constrain model behaviour
- Define clear system prompts that outline the model’s role, capabilities, and limitations.
- Prevent the model from switching personas or tasks based on user input.
- Use session resets to avoid accumulation of malicious context.
- Define and enforce output formats
- Use fixed response templates to prevent deviation into unsafe behaviours.
- Validate outputs against safe patterns before displaying them to users.
- Implement input validation and filtering
- Apply regex and NLP filters to detect encoded or obfuscated malicious prompts (e.g., Base64, Unicode tricks).
- Escape special characters, limit input size, or rate-limit repeated submissions.
- Enforce least privilege access
- Ensure the AI system has only the minimum permissions required for its tasks.
- Use sandboxed environments and role-based access control (RBAC).
- Require human oversight for high-risk actions
- Include human-in-the-loop reviews for sensitive actions involving data or system changes.
- Maintain audit logs of outputs that trigger actions and human approvals.
- Segregate and identify external content
- Label whether content originates from trusted internal or untrusted external sources.
- Process untrusted content separately with stricter scrutiny.
- Conduct adversarial testing and simulations
- Regularly simulate prompt injection attacks (red-teaming) to identify vulnerabilities.
- Update system prompts and policies based on test results.
- Monitor and log AI interactions
- Capture logs of user inputs, model responses, and interactions.
- Use anomaly detection to flag attempts to override system instructions.
- Regularly update security protocols
- Continuously refresh system prompts, filters, and access controls as threats evolve.
- Test updates in sandbox environments before deployment.
- Train models to recognise malicious input
- Use adversarial training (e.g., reinforcement learning with human feedback) to improve resilience.
- Continuously update adversarial examples and classifier models.
- User education and awareness
- Educate users about social engineering tactics used in prompt injection attacks.
- Encourage users to verify unusual AI outputs and escalate when needed.
Why It Matters for Organisations
As enterprises increasingly adopt generative AI for automation, analytics, and decision-making, prompt injection represents a real and rising threat. Since LLMs interpret both developer and user input together, they can be manipulated to act unpredictably.
For organizations, this can mean the following:
- Exposure of sensitive data, leading to regulatory penalties.
- Erosion of trust in AI systems that produce misleading or harmful content.
- Operational disruption, if AI triggers unintended commands.
- Reputation risk, if compromised AI spreads misinformation or leaks data.
To counter these risks, StrongBox IT helps organisations integrate AI security at every stage of deployment—ensuring resilience against prompt injection and preserving trust in AI-driven operations.
Conclusion
Prompt injection attacks underscore the importance of securing AI-driven systems against manipulation and data compromise. As large-language models continue to support business functions, even subtle vulnerabilities can have significant consequences. Implementing layered protection—like prompt validation, input sanitisation, access controls, and continuous monitoring—helps preserve system integrity. Regular audits and employee awareness further strengthen defence against evolving threats.
For advanced protection against AI-related attacks, connect with StrongBox IT to secure your organisation’s digital systems.





